Departments
Medical Surgical Nursing
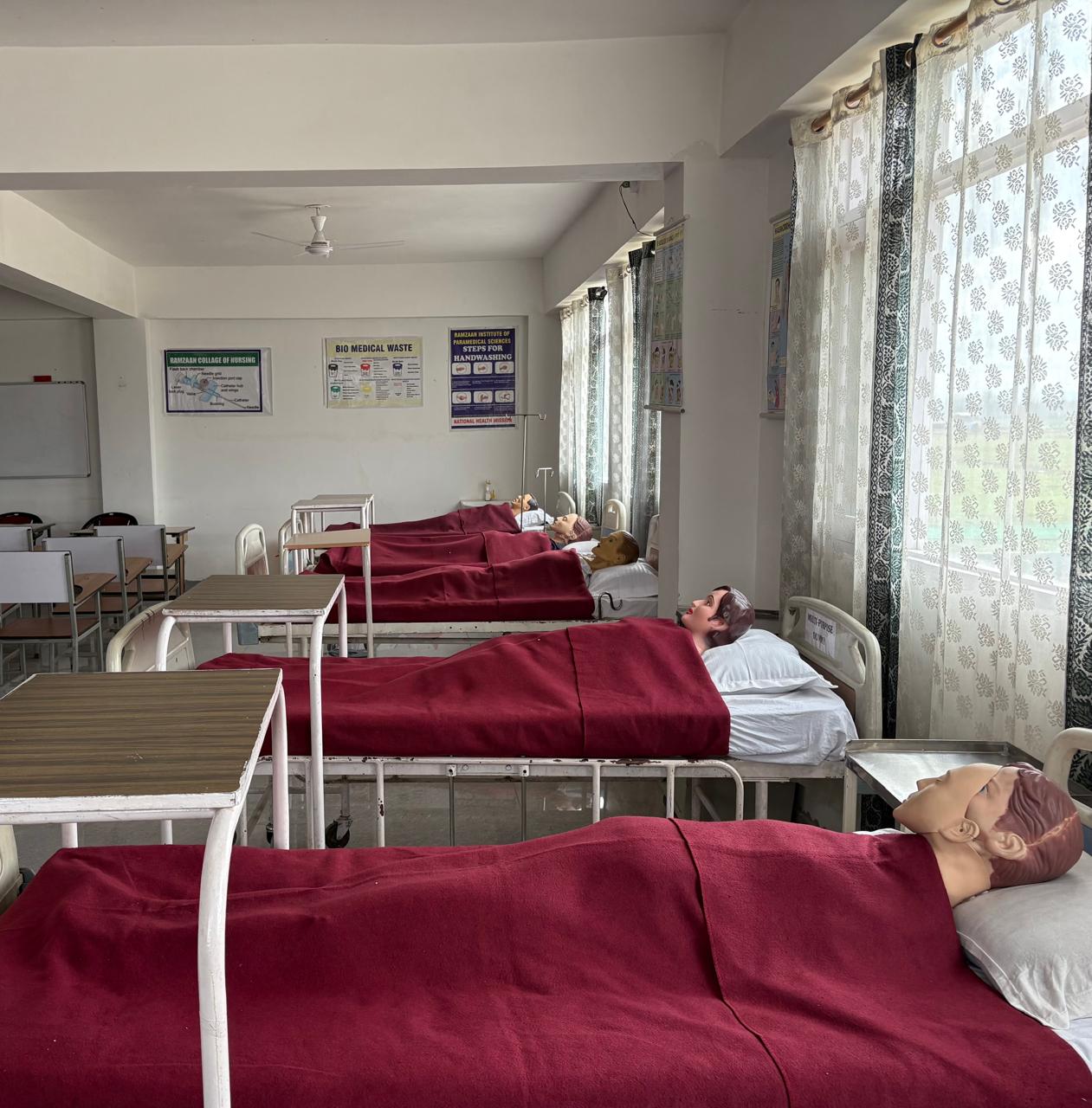
A Medical Surgical Nursing (MSN) department focuses on providing comprehensive care to adult patients with medical and surgical conditions. It prepares students to become nurses, educators, managers, and researchers in this specialized field. The department typically covers topics like medical and surgical conditions, diagnostic procedures, treatment modalities, and the nursing process.
Key aspects of a Medical Surgical Nursing department:
- Curriculum:The curriculum covers a wide range of medical and surgical conditions, including those affecting various organ systems. It also emphasizes the nursing process (assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation).
- Clinical Skills:Students gain practical experience in providing care to patients with various medical and surgical conditions, including medication administration, wound care, and using medical equipment.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration:The department fosters teamwork and collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, surgeons, and therapists.
- Research and Evidence-Based Practice:Students are encouraged to engage in research and apply evidence-based practices to improve patient care.
- Career Opportunities:Graduates can find employment in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, and physician practices, as medical-surgical nurses, educators, managers, or researchers.
Examples of topics covered in an MSN department:
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, cardiovascular disease, respiratory disorders, infections, and neurological conditions.
- Surgical conditions: Orthopedic surgery, general surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and urological surgery.
- Nursing Process: Assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
- Patient education: Providing patients and their families with information about their conditions, treatments, and self-care.
- Medication administration: Ensuring safe and effective medication administration.
- Wound care: Providing proper wound care to prevent complications.
- Communication and teamwork: Effective communication with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals.